https://www.giid.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/What-are-IDs-cover-image.jpg
640
1920
Federico Jorge
https://www.giid.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/Global-Institute-on-Innovation-Districts-logo-color.png
Federico Jorge2024-07-17 09:03:142024-07-26 14:50:54Protected: What are Innovation Districts?
https://www.giid.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/What-are-IDs-cover-image.jpg
640
1920
Federico Jorge
https://www.giid.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/Global-Institute-on-Innovation-Districts-logo-color.png
Federico Jorge2024-07-17 09:03:142024-07-26 14:50:54Protected: What are Innovation Districts?Six ways for innovation districts to build welcoming, safe, integrated places
Innovation districts face a multi-dimensional challenge: how to create an exciting, educational, safe, and inclusive place. These qualities are essential to innovation districts—hyperlocal geographies that typically combine academic and medical institutions, corporate R&D centers, startups, and entrepreneurial support organizations, clustered in mixed-use communities to encourage creativity, collaboration, and innovation.
Creating a welcoming place isn’t easy. A district’s landscape may feel sterile or uninviting to residents and to a community, with many activities and events hidden from view inside buildings and labs. Transforming such environments requires a thoughtful approach: understanding what a community wants, taking time to experiment with public spaces and places, and identifying creative ways for financing activities to help residents feel ownership of the space.

An example of a parklet, which can transform a street and make it more welcoming. Source: University City District.
Download the PDF with the innovative practice guide or click on this link to view the guide in your browser: Six ways for innovation districts to build welcoming, safe, integrated places
Australia’s pathway to innovative growth lies with its universities
Fifteen years from now will Australia be known for its global contribution in commodities or its repositioning as a rising star in innovative growth?
If Australia is to become a rising star, it will require a set of structural reforms at the federal level in areas such as education, tax regulation, and industrial policy. Yet one of Australia’s first moves should be to transform its R&D-laden universities to become hyper-compact, connected, and collaborative locales of spiking innovative growth.
Brookings research describes how a growing emphasis on collaboration is contributing to a new geography of innovation called innovation districts, or innovation precincts, across all global regions. In these enclaves, research-laden anchor institutions and companies cluster within close quarters to foster the conditions that lead to innovative growth.
Statistics on Australia’s universities indicate the true potential of these institutions to anchor successful innovation precincts. For example, the Academic Ranking of World Universities now ranks 23 Australian universities in the top 500 worldwide—up from 13 in its inaugural ranking in 2003. Furthermore, the 2016 Australian Innovation System Report reveals that Australia’s higher education sector provides the vast majority of Australia’s basic research as well as an important share of applied research—both of which are critical to innovative growth. This same report also cites the volume and quality of universities’ academic publications. In engineering and natural sciences, Australian publications account for a greater share of the top one percent of highly cited publications than the OECD average.
Put simply, Australia’s universities have the research chops to become a driver of innovative, market-led growth.
Even as Australia’s universities grow in stature, other broader economic trends are giving cities, including their universities, a new chance to compete. In today’s innovation landscape, no one company can master all the knowledge it needs, requiring companies and other organizations to rely on a network of industry collaborators. This in turn has placed a growing premium on collaboration and the convergence of multiple minds and disciplines. This is as true in Australia as elsewhere; the Innovation System Report found that Australian businesses that collaborated on innovation “were twice as likely to develop ten or more innovations in 2014–2015.
Put simply, Australia’s universities have the research chops to become a driver of innovative, market-led growth.
To date, two of the most successful of Australia’s innovation precincts have been spearheaded by the University of Melbourne. One of Australia’s top-ranked universities, Melbourne is a particular standout in life sciences and physical sciences and is now surrounded by a growing cluster of companies, startups, and a range of innovation spaces.
Melbourne’s biomedical precinct is home to over 10,000 scientists, clinicians and technical staff, all within a walkable one-kilometer (0.62-mile) radius. Spin-offs from this precinct have included a $560 million deal for drugs to alleviate conditions relating to fibrosis and a $198 million deal for its innovative head lice product. Carlton Connect, the second precinct within Melbourne’s innovation ecosystem, aims to supercharge its innovation by leveraging proximity and partnerships—a particularly striking challenge for Australia given that the country ranked last in the OECD for industry-research collaborations.
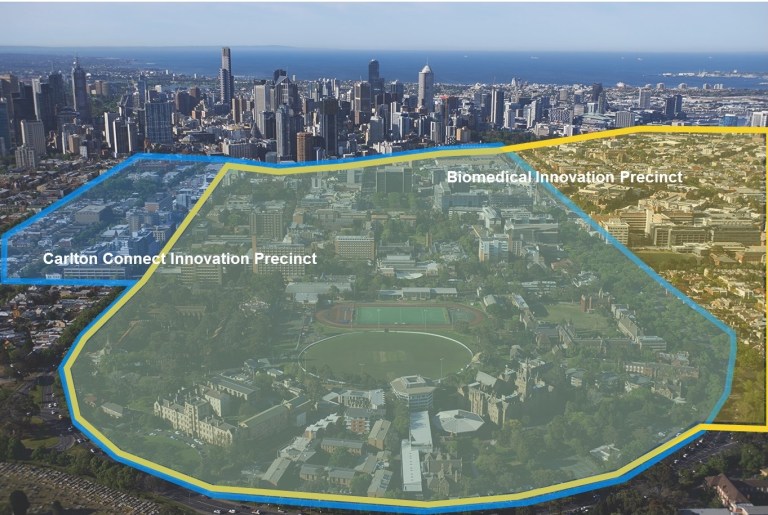
Two innovation precincts spearheaded by the University of Melbourne. Photo courtesy: Carlton Connect; boundaries illustration by Brookings
The University of Melbourne is part of the Group of Eight—a coalition of Australia’s leading universities. These eight institutions are ripe for this kind of local innovation play: leveraging their research strengths and international networks, stimulating spin-offs, and using land to create new innovation spaces for new partnerships. For these eight, opportunities abound.